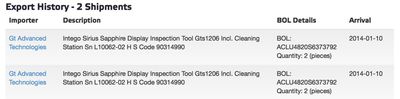
GT Advanced, the company that has partnered with Apple to open a sapphire plant in Mesa Arizona, has purchased and received a total of 518 sapphire furnace and chamber systems with another 420 machines on order, according to analyst Matt Margolis (via 9to5Mac). The company has also purchased multiple "Sapphire Display Inspection Tools" from Intego.
The sheer amount of equipment purchased indicates that a massive sapphire production operation is being installed at the Arizona factory, and as rumors have hinted, the large amounts of sapphire being produced, along with the tools ordered, could hint at a future ultra-durable iPhone display.
Matt Margolis believes that with the current equipment the factory has, it could produce between 103 and 116 million displays per year, with an additional 84 to 94 million possible when taking into account the 420 furnaces on order. Apple could, in total, produce 100 to 200 million ~5-inch sapphire displays, enough for its entire line of devices. In 2013, Apple sold approximately 150 million iPhones.
In documentation, GT Advanced itself suggests the aforementioned Sapphire Inspection Tools are aimed at device displays.
Lowering manufacturing and fabrication costs of sapphire is a key driver for accelerating the adoption of its use in new market segments such as cover screens for smartphones and mobile devices. GT Advanced Technologies is working with key downstream technology providers to optimize fabrication processes and technologies to lower the cost of sapphire cover screen material.
GT is partnering with Intego GmbH to develop a series of automated sapphire inspection tools that will increase the yield of high quality sapphire material from each boule and ensure that only high quality material enters the value stream. The SIRIUS Slab automated sapphire inspection tool begins a new level of repeatability and performance throughput to the production of sapphire material intended for high volume markets such as mobile and touch screen devices.
In November, shortly after the partnership between GT Advanced and Apple was announced, it became clear that GT Advanced, with Apple's help, was aiming to drastically increase its sapphire production.
A recent patent pointed to Apple's interest in using sapphire as a display cover on future iPhones and shortly after, a report suggested Apple partner Foxconn had already began a small trial production of 100 devices with a sapphire display.
Those rumors, along with today's report, indicate that Apple is almost certainly aiming to use sapphire as a major component in an upcoming product such as the next-generation iPhone or the company's much-rumored iWatch. Currently, the company uses limited quantities of sapphire to protect the camera on recent iPhones and to cover the Touch ID fingerprint sensor on the iPhone 5s.
Sapphire, as the second hardest mineral after diamond, is incredibly durable and scratch resistant, as can be seen in the video below. An iPhone with a sapphire display would be almost impossible to scratch in day-to-day use.
Apple and GT Advanced are said to be aiming to take the Mesa, Arizona plant live by February in order to begin immediate production of a "critical new sub-component" for iOS devices.


















Top Rated Comments
Don't say it too loud, or them keys in your pocket might get jingly. To be frank, it takes just one scratch to ruin the look of such an expensive device. Kudos to Apple that they are going the extra mile.
You barely saw any scratches does not mean no one else did.
What confuses people is that they often refer to the Mohs hardness scale, which rates hardness in relation to ten common minerals. In that list, yes, sapphire is reference mineral #9, and diamond is reference #10.
But that does not mean there's nothing in-between them.
Materials such as silicon carbide (carborundum aka the mineral moissanite), tungsten carbide, titanium carbide, boron, boron nitride, rhenium diboride, stishovite, and titanium diboride ARE HARDER THAN SAPPHIRE. That is, they are 9+ on the Mohs scale.
For that matter, there are now materials harder (10+ on the scale) than diamond .
I don't think thinner will work. As I keep pointing out, to prevent easy breakage, sapphire watch crystals are from 3-6 times as thick as what's used for Gorilla Glass phone covers. And watches are a small area.
Sapphire also weighs about 60% more than GG.
This is no doubt why we see Apple patents on joining very thin sapphire sheets to glass. That way, you get the scratch resistance of sapphire on top, and the structural strength and weight savings of the glass substrate.
Since when were you allowed to brag about how you were right based on a rumor?
Ok, here we go.
I pass this along as I am passionate on this matter, I do not want to leave a caustic planet to my children, nor do I want to destroy the oceans and wildlife that are negatively impacted by our out of control consumerism and waste. I know this is a long post, but it's a quick read and so important to all of us. Please take the moment :)
Every year, Americans throw away enough paper and plastic cups, forks, and spoons to circle the equator 300 times (http://www.cleanair.org/Waste/wasteFacts.html). Plastic produces more waste from recycling and general consumer discard. Recycling produces more pollutants, including chemical stews when breaking down different products.
Recycling is not cost-efficient and annually results in a net loss. It costs $50-60 to landfill a ton versus $150+/- to recycle. Only the recycling of aluminum really makes any money. Reclaiming metals is feasible and fairly easy, whereas plastics and paper are expensive, wasteful and overly difficult. The biggest disadvantage to recycling is that it gives the consuming public a false sense of 'security'; a sense that they're doing something to benefit the environment. recycling can be bad for the environment. In fact, except for materials like metal and some glass, recycling is almost always bad for the environment. One of the best places to start is with a report from Perc.org, called the Eight Great Myths of Recycling (http://perc.org/sites/default/files/ps28.pdf). "One argument made for recycling notes that we live on a finite planet. With a growing population, we must, it seems, run out of resources."
E-waste is a major issue, especially with plastics. There are 2 plastic islands the size of Texas, one in the Pacific Ocean - the "Great Pacific garbage patch" (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Great_Pacific_garbage_patch)and one in the Indian Ocean (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indian_Ocean_garbage_patch) and more being discovered almost monthly.
Charles Moore - TED discussion on plastic (//www.youtube.com/watch?v=en4XzfR0FE8) - 7 minutes but alarming facts on plastic toxicity and huge annual increases in waste.
As Japan has serious garbage issues, a Japanese scientist invented a machine that breaks any plastic down into oil! I've mentioned the on MacRumors before as it is an issue the tech industry needs to take into serious consideration. This device is no larger than a microwave and uses less energy than a coffee maker. Read and watch the short 5 min video, if for nothing else than the tech as it's amazing. Hoping quick mainstream adoption lowers the $10k price tag quickly enough for residential use and can make up for its price by reusing the oil. Used in large industrial recycling centers would be amazing!
Plastic to oil fantastic (http://ourworld.unu.edu/en/plastic-to-oil-fantastic/)
Aluminum is currently the best material for mass production in products, especially tech due to e-waste. Bauxite being the most common aluminum ore. Refinement uses much less energy to produce, and is improving with recent advancements, especially compared to the Hall-Héoult Process (the major industrial process aluminum extraction). Aluminum is theoretically 100% recyclable without any loss of its natural qualities and requires only 5% of the energy used to produce aluminum from ore, though a significant part (up to 15% of the input material) is lost as dross (ash-like oxide). Recycled aluminum is known as secondary aluminum, but maintains the same physical properties as primary aluminum. Secondary aluminum is produced in a wide range of formats and is employed in 80% of alloy injections. The process produces aluminum billets, together with a highly complex waste material, which can be reused as a filler in asphalt and concrete.
To answer your question, that is why it is important. I mean this sincerely, not sarcastically, read up on the matter, do some research - the statistics are alarming but hopeful if all of us work together.
If you got this far, thank you. Collectively we can make a difference in plastic usage by "voting with our dollars". We don't need more waste; plastic in tech produces much more waste (and chemical waste from wires, displays, etc) than other naturally occurring metals and smelting. It's great Apple is trying to produce a lower cost iPhone, however plastic shouldn't be much cheaper than smelting aluminum, especially as Apple has dedicated plants for product shells using green energy.